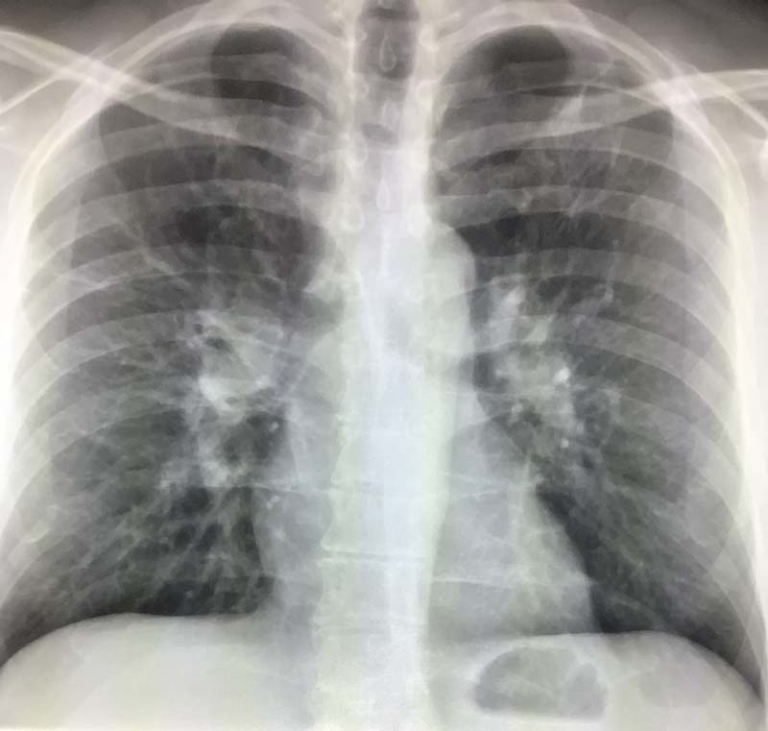
What Does Perihilar Mean?
The term “perihilar” is used to describe findings near the hilum of the lungs on studies like X-rays and CT scans. The perihilar region is an important area where important structures like the bronchi, blood vessels, and lymph nodes are located. Understanding what perihilar means can help make sense of imaging results and potential underlying conditions.
What Does Perihilar Mean in Medical Imaging?
The term “perihilar” refers to the area surrounding the hilum, which is the central part of the lungs where the main airways (bronchi), pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and lymph nodes are located. This region is important for lung function because it serves as the primary gateway for air and blood to enter and leave the lungs.
On a chest X-ray or CT scan, radiologists use the term “perihilar” to describe abnormalities in this area. This could be due to a variety of conditions, ranging from infections to more serious lung diseases like cancer.
Common Perihilar Findings on Imaging
1. Perihilar Opacities
Perihilar opacities refer to areas that appear denser or whiter than normal on an X-ray or CT scan. These opacities can be caused by fluid, infection, inflammation or other abnormalities affecting the lung tissue. Common causes include:
- Pneumonia – Infections like bacterial or viral pneumonia can cause inflammation and fluid accumulation in the perihilar region.
- Pulmonary edema – Fluid buildup in the lungs, often due to heart failure, can present as perihilar opacities.
- Lung fibrosis – Scarring of lung tissue can cause thickening and increased density in the perihilar area.
2. Perihilar Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy refers to enlarged lymph nodes. When lymph nodes in the perihilar region become enlarged, it could indicate:
- Infections – Conditions like tuberculosis or fungal infections can cause lymph node swelling.
- Sarcoidosis – This inflammatory disease often leads to symmetrical enlargement of perihilar lymph nodes.
- Lung cancer – Some lung cancers can spread to perihilar lymph nodes, leading to enlargement.
3. Perihilar Vascular Congestion
Perihilar vascular congestion occurs when there is increased blood flow or pressure in the lung’s blood vessels. This is often seen in conditions such as:
- Heart failure – The heart’s inability to pump efficiently can cause blood to back up into the lungs, leading to perihilar congestion.
- Pulmonary hypertension – High pressure in the lung arteries can cause prominent perihilar vessels on imaging.
How Radiologists Interpret Perihilar Findings
Radiologists analyze perihilar changes by looking at factors like symmetry, size, and density of the abnormalities. Key considerations include:
- Is the finding on one side or both? Unilateral findings may suggest infection or localized disease, while bilateral changes could indicate systemic conditions like heart failure or sarcoidosis.
- Are the blood vessels enlarged? This could suggest vascular congestion from heart-related issues.
- Is there associated lung involvement? If other areas of the lung appear abnormal, the perihilar changes might be part of a larger disease process.
Personal Insight:
In my practice, perihilar findings are most often linked to heart failure or infections. When I see perihilar congestion, I always check for signs of fluid overload, such as an enlarged heart or pleural effusions. This helps guide further testing and treatment decisions.
Conditions That Can Cause Perihilar Abnormalities
1. Pneumonia
Pneumonia can cause perihilar opacities due to infection and inflammation in the lungs. Viral pneumonia, particularly from influenza or COVID-19, often affects the perihilar region, creating a hazy or patchy appearance on imaging.
2. Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema
In congestive heart failure, the heart struggles to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs. This often presents as perihilar congestion, with a characteristic “butterfly” pattern on chest X-rays.
3. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that commonly affects the lungs. A hallmark of this condition is bilateral perihilar lymph node enlargement, which can be detected on chest X-rays or CT scans.
4. Lung Cancer and Metastatic Disease
Lung cancer can cause perihilar masses or lymphadenopathy. Some cancers originate in the perihilar region, while others spread to nearby lymph nodes, altering the normal structure of the hilum.
When to Be Concerned About Perihilar Findings
Not all perihilar findings indicate a serious problem, but certain patterns may require further investigation:
- Rapidly growing masses – Could indicate cancer or aggressive infections.
- Severe congestion with fluid buildup – May suggest worsening heart failure.
- Enlarged lymph nodes without infection – Could be a sign of lymphoma or other malignancies.
If your radiology report mentions perihilar findings, it’s important to follow up with your doctor for further evaluation and possible additional tests, such as CT scans, blood work, or biopsy.
Conclusion
The term “perihilar” on a radiology report simply refers to findings near the central part of the lungs. While perihilar changes can be caused by infections, heart conditions, or even cancer, their significance depends on the context of the patient’s symptoms and appearance on imaging. Radiologists carefully assess these findings to help guide further testing and treatment. If you receive a report mentioning perihilar abnormalities, discussing it with your doctor can help clarify what it means for your specific situation.
References