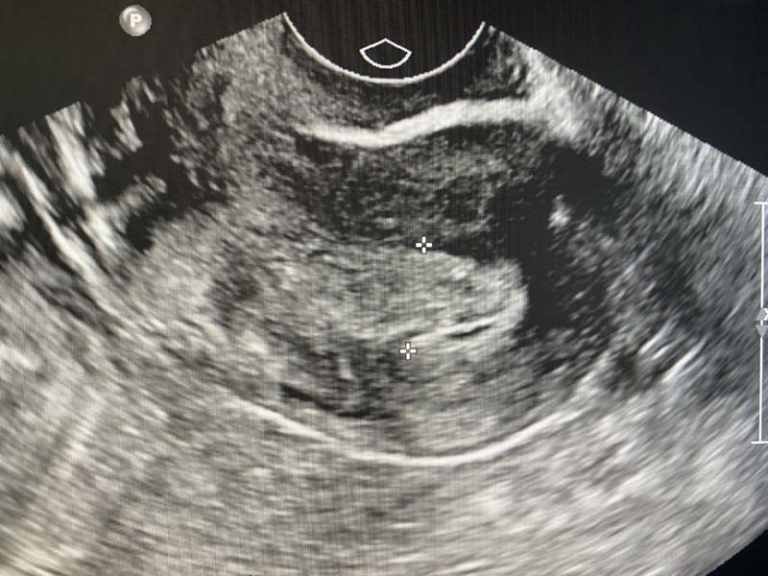
Iliac Artery Aneurysm
Iliac artery aneurysm is a vascular condition that involves a weakened area in the iliac artery, a major blood vessel in the pelvis. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition is important for early detection and effective management.
What is Iliac Artery Aneurysm?
An iliac artery aneurysm occurs when there is a bulging or ballooning of the iliac artery. This condition is often asymptomatic, making it challenging to detect without proper imaging tests. The enlargement of the artery can lead to potential complications such as rupture, causing severe internal bleeding.
Symptoms of Iliac Artery Aneurysm:
In most cases, iliac artery aneurysms do not present noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic region may occur due to pressure on surrounding tissues.
- Pulsating mass: A pulsating sensation or lump may be felt in the abdomen or groin area.
- Leg pain or numbness: Reduced blood flow to the legs due to the aneurysm can cause pain, weakness, or numbness in the legs.
Diagnosing Iliac Artery Aneurysm:
Iliac artery aneurysms often remain asymptomatic, making their detection challenging without proper imaging. Diagnostic imaging not only confirms the presence of an aneurysm but also determines its size, location, and potential complications. Timely and accurate imaging aids healthcare providers in devising appropriate treatment strategies to manage this condition.
Imaging Techniques for Iliac Artery Aneurysm:
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging, also known as duplex ultrasonography, is a non-invasive technique that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of blood flow in the iliac arteries. It helps in identifying the presence of aneurysms, assessing their size, and monitoring blood flow patterns. This technique is commonly used as an initial screening tool due to its convenience and safety.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the iliac arteries using X-rays and computer technology. This imaging method offers high-resolution images that assist in accurately visualizing the size, shape, and location of iliac artery aneurysms. It allows healthcare providers to precisely measure the dimensions of the aneurysm and plan appropriate treatment options.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the blood vessels without radiation exposure. This imaging modality is valuable for evaluating iliac artery aneurysms, providing comprehensive information about the blood flow, surrounding tissues, and the aneurysm’s structural characteristics. MRI aids in assessing the potential risk of rupture and determining the need for intervention.
- Angiography: Angiography involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels followed by X-rays to visualize the arteries’ structure and blood flow. This technique helps in obtaining precise images of the iliac arteries, allowing healthcare professionals to identify the exact location and severity of the aneurysm.
- 3D Reconstruction Imaging: Advanced imaging technology allows for the creation of 3D reconstructions based on CT or MRI scans. These three-dimensional models provide enhanced visualization of the iliac arteries and the aneurysm, assisting surgeons in planning procedures and navigating complex vascular anatomy with greater precision.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for iliac artery aneurysms depends on various factors, including the size of the aneurysm, the patient’s overall health, and the risk of rupture. Treatment options may include:
- Monitoring: Small aneurysms with a low risk of rupture may be regularly monitored through imaging tests to track any changes in size.
- Surgery: For larger aneurysms or those at risk of rupture, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve open repair or endovascular repair, where a stent graft is placed inside the artery to reinforce the weakened area.
- Medications: Physicians may prescribe medications to manage symptoms or reduce the risk of complications associated with iliac artery aneurysms.
Preventing Iliac Artery Aneurysm:
While some risk factors for developing iliac artery aneurysms, such as age and family history, cannot be controlled, certain measures may help reduce the risk:
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise routine, and avoiding smoking can contribute to overall vascular health.
- Regular check-ups: Periodic medical check-ups enable early detection of any potential vascular issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Conclusion:
Iliac artery aneurysm, though often asymptomatic, can pose serious health risks if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and utilizing appropriate imaging techniques are crucial steps in diagnosing and managing this condition. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with iliac artery aneurysms can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
Remember, early detection through imaging tests and consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for addressing iliac artery aneurysms and ensuring optimal vascular health.